- 1. Injections
Done by : Mohammed A Qazzaz
- 2. Routes of Medication Administration
Parenteral medication: administration of a medication
by injection into body tissues
Subcutaneous (SC) – into tissue below dermis of skin
Intramuscular (IM) – into the body muscle
Intravenous (IV) – into a vein
Intradermal (ID)– into the dermis just under the
epidermis
- 3. What is an injection?
Injections are sterile solutions,
emulsions or suspensions.
They are prepared by dissolving,
emulsifying or suspending an active
ingredient and any other substances in
water for injection.
Injecting is the act of giving medication
by use of syringe and needle to obtain
the desired therapeutic effect taking into
account the patients safety and comfort
- 4. How are drugs for injections presented?
Single dose preparations
a pre - prepared volume of measured drug, in a
syringe for single dose use
i.e. Flu vaccines, Pneumovax and B12.
Multidose preparations
multi-dose preparations contain a
antimicrobiacteral preservative, are used on
more than the one occasion and great care is
required for its administration but especially it’s
storage between successive withdrawals
i.e Insulin
- 5. Why give drugs in injection form
Injections usually allow rapid absorption
Can produce blood levels comparable to those
of intravenous bolus injections
Injections can be given from 1ml and up to 2
mils in the Deltoid and up to 3 mls in the
gluteal muscle in adults
Drugs that are altered or not absorbed by
other methods of administration
- 6. Needle length and size
For intramuscular injections e.g flu, pneumonia
and B12, the needle should be long enough to
penetrate the muscle and still allow a quarter of
the needle to remain external to the skin
When choosing the needle it is important to
assess the amount of muscle, subcutaneous fat
and weight of the patient - which in the majority
of cases will be a blue needle
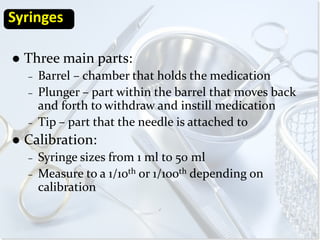
- 7. Syringes
Three main parts:
– Barrel – chamber that holds the medication
– Plunger – part within the barrel that moves back
and forth to withdraw and instill medication
– Tip – part that the needle is attached to
Calibration:
– Syringe sizes from 1 ml to 50 ml
– Measure to a 1/10th or 1/100th depending on
calibration
- 8. Needles
Shaft of the needle
– Length chosen depends on the depth to
which medication will be instilled
– Tip of shaft is beveled or slanted to pierce
the skin more easily
Gauge: width ofthe needle (18 – 27
gauge) – a smaller number indicates a
larger diameter and larger lumen inside
the needle
- 9. Considerations when choosing a syringe and
needle
Type of medication
Depth of tissue penetration required
Volume of medication
Viscosity of medication
Size of the client
- 10. Which is which needle?
The correct needle is the key to delivering the drug to
the correct area for the maximum effect with the least
amount of discomfort
The colour at the top of the needle reflects its size
the higher the number the smaller the lumen (bore)
Orange needles = 25 gauge = 10mm long (3/8 inch)
or 16mm long(5/8 inch) or 25mm long (1 inch)
Blue needles = 23 gauge = 25mm long 9 (1 inch)
Green needles = 21 gauge = 38mm long (1.5 inches)
- 13. Equipment for the administration of injections
Clean tray or receiver in which to place drug and equipment
21g needle to ease reconstitution and drawing up (23g if from a glass
ampoule
Syringe of appropriate size
Swabs saturated with isopropyl alcohol 70%
Sterile topical swab if drug is presented in ampoule form
Drug to be administered
Patients prescription to check dose, route and timing
Notes available to record administration in accordance with law
Gloves, Apron
- 14. Clinical room preparation for the administration
of injections
Protocols/procedure/standards information is
available
Hand basin for washing hands and/or alcohol
hand rub.
Area for the client to lie down if unwell
Panic button/phone to call for assistance
sharps container
Gloves
Resuscitation /anaphylaxis equipment/drugs
Oxygen and appropriate mask if available
adequate time for procedure
- 15. Asepsis and reducing the risk of infection
Good hand washing
Good hand drying
Aseptic technique
Good observation and questioning
of the client
Skin preparation if required
- 16. The 7 Rights of Drug Administration
Right client
Right medication
Right dose
Right route
Right time
Right reason
Right documentation
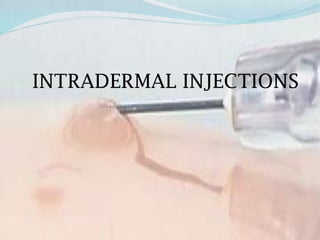
- 17. INTRADERMAL INJECTIONS
- 18. INTRADERMAL INJECTIONS
Most often used for PPD
Site: the inner aspect of the forearm
Needle size is 25 - 27 gauge, 1/2 to 5/8 inch
Insert needle at 15o angle
Injection made just below the outer layer of skin
If injection does not form a wheal or if bleeding is
noted, the injection was probably too deep and
should be repeated
- 19. INTRADERMAL INJECTIONS
Review the provider’s order for accuracy
Ask the patient/parent if the patient is allergic to the
medication
Wash your hands and gather supplies, equipment
Select proper needle size, length and gauge
- 20. INTRADERMAL INJECTIONS
6 Rights of medication administration
Check the expiration date of the medication
Check for discoloration etc., discard if questionable
- 21. INTRADERMAL INJECTIONS
Explain procedure to patient/parent
Ask for assistance with children
Position patient appropriately
Prepare injection site with alcohol - air dry
Support skin with thumb
With bevel up, completely insert bevel at a 15 o angle
- 22. INTRADERMAL INJECTIONS
Inject medication gently, place a cotton ball over the
site after needle removal
A visual wheal will be produced at the site
Dispose of needle as per policy
Wash hands
Document procedure and patient’s response
- 23. INTRADERMAL INJECTIONS
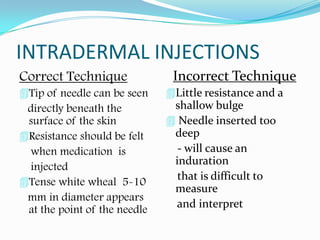
Correct Technique Incorrect Technique
Tip of needle can be seen Little resistance and a
directly beneath the shallow bulge
surface of the skin Needle inserted too
Resistance should be felt deep
when medication is - will cause an
injected induration
Tense white wheal 5-10
that is difficult to
measure
mm in diameter appears
at the point of the needle and interpret
- 25. Subcutaneous
injection
- 26. Insulin is the most important
drug in the subcutaneous
injections
- 27. Insulin
Insulin
Indications
Type I diabetes mellitus, type II diabetes mellitus,
Indications
hyperkalemia, DKA/diabetic coma
Type I diabetes mellitus, type II diabetes mellitus, hyperkalemia,
DKA/diabetic coma
MOA
Stimulating peripheral glucose uptake and inhibiting
MOA
hepatic glucose production uptake and inhibiting hepatic
Stimulating peripheral glucose
glucose production
Patient Info
Patient Info
Hypoglycemia (BG < 70 mg/dL) esp with higher doses
Hypoglycemia (BG < 70 mg/dL) esp with higher doses
– Anxiety, blurred vision, palpitations, shakiness, slurred
– Anxiety, blurred vision, palpitations, shakiness, slurred
speech, sweating
speech, sweating
Weight gain
Weight gain
- 28. Where does it work?
- 29. Insulin (cont)
Administration:
Subcutaneous injection
Rotate site
Check blood sugars regularly
Storage:
Refrigerate until use
Once vial is punctured, it is good for 28 days
and can be left at room temperature (except
for glargine which is 90 days)
- 30. Insulin (cont)
Dosing:
Starting daily dose: 0.5-1 unit/kg/day in divided doses
Adjust according to fasting (premeal) blood glucose of 80-130
mg/dL and peak postprandial blood glucose < 180 mg/dL
Provide 50% as long acting insulin and 50% as prandial insulin
1 unit of can account for 30 grams of carbohydrate (14-50)
1 unit can lower 50 mg/dL blood glucose (10-100)
Special Population Consderations:
Renal dysfunction
– CrCl 10-50 mL/min: 75% of normal dose
– CrCl < 10 ml/min: 25-50% of normal dose; monitor closely
Exercise??? ---- Acute Stress???
- 31. Insulin Action
Rapid/immediate
Intermediate
Blood concentration
Fast
Slow
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24
Time (hr)
- 32. Insulin Dosing
Long-acting
Long-acting &
Short-acting
Normal insulin secretion
70/30
pre-mixed
- 33. Insulin Administration
- 34. Insulin (cont)
Cautions/Severe Adverse Reactions
Severe hypoglycemia (seizure/coma) (BG < 40
mg/dL)
Edema
Lipoatrophy or lipohypertropy at injection site
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Severe hypoglycemia
Allergy or sensitivity to any ingredient of
the product
- 35. SUBCUTANEOUS INJECTION
- 36. INTRAMUSCULAR
INJECTION
- 37. INTRAMUSCULAR INJECTION
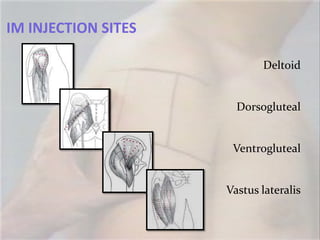
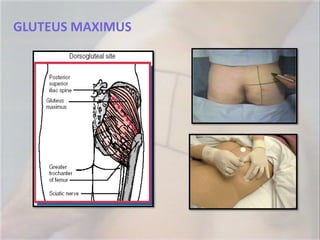
- 38. IM INJECTION SITES
Deltoid
Dorsogluteal
Ventrogluteal
Vastus lateralis
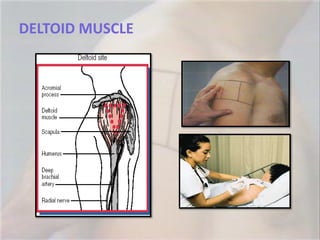
- 39. DELTOID MUSCLE
- 40. GLUTEUS MAXIMUS
- 41. GLUTEUS MEDIUS
- 42. VASTUS LATERALIS
Institute of Nursing Theory and Practice, Prague
2007
- 43. Intramuscular Injections and Pain
The needle
The technique
The speed of the injection
The solution and composition of the drug
The volume of the drug
The approach and attitude of person
administering the injection