- 1. A Seminar On Vibration Analysis And Damping In
Structures
Submitted to: Submitted By:
Mr Rahul Bhaiji Divya Lattoo
Utkarsh Tiwari
- 2. Introduction
Structure –
A structure is a combination of parts fastened together
to create a supporting framework, which may be part of
a building, ship, machine, space vehicle, engine or
some other system.
Vibrations –
- 3. THE CAUSES AND EFFECTS OF
STRUCTURAL VIBRATION
Cause
Effect
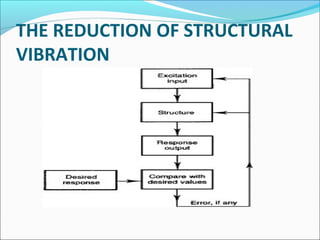
- 4. THE REDUCTION OF STRUCTURAL
VIBRATION
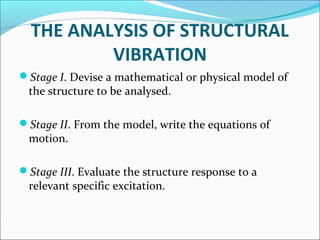
- 5. THE ANALYSIS OF STRUCTURAL
VIBRATION
Stage I. Devise a mathematical or physical model of
the structure to be analysed.
Stage II. From the model, write the equations of
motion.
Stage III. Evaluate the structure response to a
relevant specific excitation.
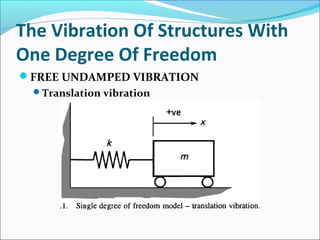
- 6. The Vibration Of Structures With
One Degree Of Freedom
FREE UNDAMPED VIBRATION
Translation vibration
- 7. Torsional vibration
- 8. Energy methods for analysis
• For undamped free vibration the total energy in the vibrating system
is constantthroughout the cycle. Therefore the maximum potential
energy V(max), is equal to the maximum kinetic energy T(max) ,
although these maxima occur at different times during the cycle of
vibration. Furthermore, since the total energy is constant,
• T + V = constant,
• d(T + V)/dt = 0
• ω = (k/m)1/2
• Condition of stability –
.
- 9. FREE DAMPED VIBRATION
The most common types of damping are
Viscous
dry friction
hysteretic
- 10. Vibration with viscous Damping
• Case 1 ζ less than 1, that is, damping less than critical
• The motion of the body is therefore an exponentially decaying
harmonic oscillation
• Case 2 ζ = 1; that is, critical damping
• Critical damping represents the limit of periodic motion; hence
the displaced body isrestored to equilibrium in the shortest
possible time, and without oscillation or overshoot.
• Case 3 ζ greater than critical,
• Since both values of s are negative the motion is the sum of two
exponential decays
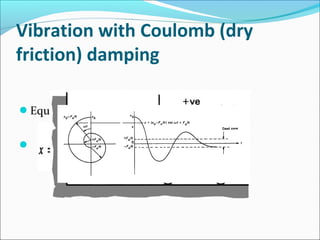
- 11. Vibration with Coulomb (dry
friction) damping
Equation Of Motion - m = Fẍ d – kx
- 12. Vibration with hysteretic damping
Experiments on the damping that occurs in solid
materials and structures that have been subjected to
cyclic stressing have shown the damping force to be
independent of frequency internal, or material,
damping is referred to as hysteretic damping.
the induced stress is σ = σ0sin (Vt+ α)
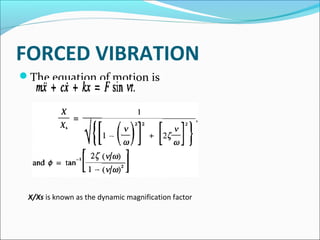
- 13. FORCED VIBRATION
The equation of motion is
X/Xs is known as the dynamic magnification factor
- 14. Resonance
The phenomenon known as resonance occurs when
the forcing frequency is equal to the natural
frequency, that is when v/ω = 1.
The maximum value of X/Xs actually occurs at values
of v/ω less than unity:
- 15. Response of a viscous damped
Structure supported on a foundation subjected
to harmonic vibration
Equation Off Motion
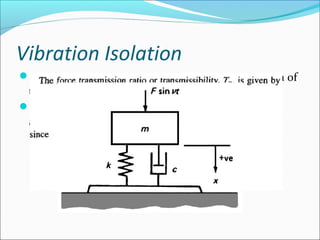
- 16. Vibration Isolation
The force transmitted to the foundation is the sum of
the spring force and the damper
force. Thus the transmitted force = kx + cẋ and Fx
the amplitude of the transmitted force is given by –
- 17. Response of a Coulomb damped structure to a
simple harmonic exciting force with constant
amplitude
The equation of motion is non-linear because the
constant friction force F, always opposes the motion:
- 18. Response of a structure to a
suddenly applied Force
The equation of motion can be written
If the structure possesses viscous damping of
coefficient c, the solution to the equation of motion is
- 19. Shock excitation
Some structures are subjected to shock or impulse
loads arising from suddenly applied, non-periodic,
short-duration exciting forces.
X(t) =
- 20. Wind- or current-excited
oscillation
A structure exposed to a fluid stream is subjected to a
harmonically varying force in a direction
perpendicular to the stream. This is because of eddy,
or vortex, shedding on alternate sides of the structure
on the leeward side.
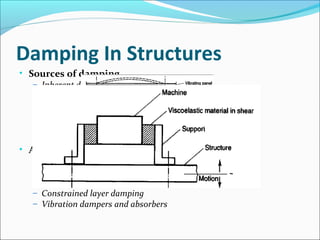
- 21. Damping In Structures
• Sources of damping
– Inherent damping
– Hysteretic or material damping
– Damping in structural joints
– Acoustic radiation damping
– Air pumping
– Aerodynamic damping
• Added damping
– High damping alloys
– Composite materials
– Viscoelastic materials
– Constrained layer damping
– Vibration dampers and absorbers
- 22. Vibration Isolation
The force transmitted to the foundation is the sum of
the spring force and the damper force.
Motion Transmission TR = X/A =
- 23. BIBLIOGRAPHY
•
Structural Vibration and Damping
By C. E Beards
www.howstuffwork.com
Theory Of Machine
By R.S.Khurmi
- 24. Questions And Query Are Welcome